Learning real crystal through the language of frequency
1. The two methods of the crystal diffraction
- Investigating through diffraction methods is based on the following idea: a crystal is exposed to the radiation source, depending on the properties of the crystals for a fixed direction, a peak will be observed in the diffraction spectrum. This methods is known as x-ray crystallography.
- Two methods to analyze the crystals:
- Bragg's method - Related to the reflection from the crystal planes
- Von Laue's method - Related to the reflection from the individual lattice sites
1.1. Bragg's method
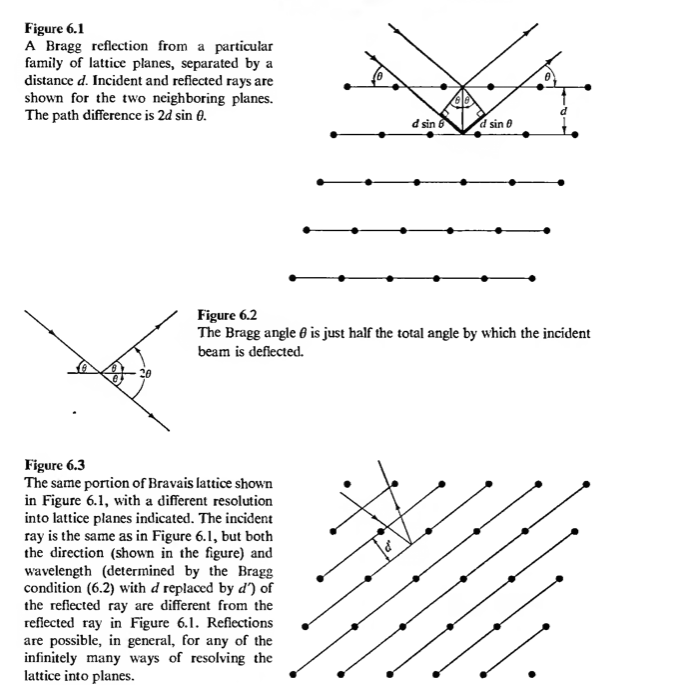
- In Bragg's method one think of the whole sample as containing crystal with planes. The Bragg's condition is
\[2d \sin \theta = n \lambda\].
- The Bragg method in picture can be described as follows:
1.2. Laue's method
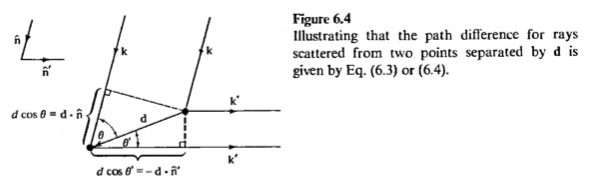
- In Laue's method every atom at each Bravias lattice site is thought to be as an antenna which radiates energy at some frequency. If \(k\) and \(k'\) are the incident and reflected beams, \(d\) is the distance between atoms, then the Laue condition can be written as:
\[d\cdot(k - k') = 2 \pi m\].
- In terms of picture the Laue's method can be described as follows:
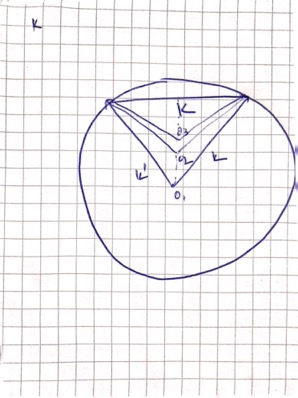
- As the incident and reflected beam has the same wavelength, then \(|k|=|k'|\). It means both \(k,k'\) represents two radius of the circle in momentum space, and \(K=k-k'\) is the line joining the two momentum vectors. In that case both \(k\) and \(k'\) will be half of the vector \(K\).
2. TODO The Edwald construction
3. Digressed Topics
3.1. Resources
- Resources for understanding crystallography:
Date: 2023-10-19 Чт 00:00
Author: Каушаль Кешарпу
Created: 2025-06-29 Вс 18:33
Validate


