The ABC of the lattice in real space
Table of Contents
1. The way to think
- To analyse the lattice structures in real space one need to understand:
- Bravias lattice
- Crystal structure
The Bravias lattice is the skeleton of the lattice structure. It gives the basic outline of the real crystal. When at each point of the Bravias lattice some ion, atoms or molecule is placed then the whole system is called the Crystal structure. Hence, if some materials is the human body, then the Bravias lattice is the skeleton. Atoms, ions or molecule placed at each node of the Bravias lattice is the flesh. In this case Human body is the crystal structure.
Bravias lattice + atoms/ion/molecule = Crystal structure Skeleton + Flesh = Human body
- The smallest unit of Bravias lattice is the primitive vectors. The smallest unit of the crystal structure is the basis.
- One can repeat the primitive vectors to create the Bravias lattice. One can repeat the basis to create the crystal structure.
- Two definition of the Bravias lattice:
- The lattice generated by the repeation of the primitive vectors is called the Bravias lattice: Brav. Lat. = \(\sum\limits_{n_{i} \in N} n_{i}a_{i}\)
- Neighbourhood of every point of the Bravias lattice is identical.
- Some of the widely studied lattice e.g. honeycomb lattice is not a Bravias lattice as neighbourhood of the every point is not the same.
2. Some other Definitions
- Coordination numbers - The number of points in the neighbourhood of the single node in Bravias lattice
- Primitive unit cell - A unit cell in Bravias lattice containing only single node.
- Unit cell - May contain more than one nodes of the Bravias lattice, but have the required symmetry for east of analysis. It differs from the primitive unit cell, as the primitive unit cell can have only single node, however usual unit cell can have more than one nodes.
- Wigner-Seitz Cell - It is the procedure to find the primitive unit cell. It has the required symmetry of the Bravias lattice.
3. Examples of the basic Bravias lattice
- The Cubic unit cell
- The BCC unit cell
- The FCC unit cell
4. Examples of the Crystal structures
- Lattice having single type of atom or ions as the basis:
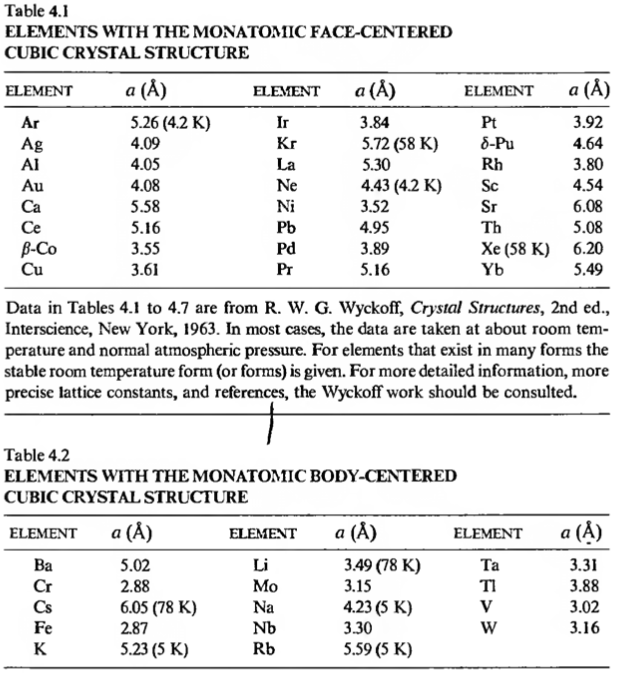
FCC and BCC structures
Some real crystal structures having BCC and FCC crystal structures:
- The hexagonal close packing structures
- The diamond structures
- Lattice having different types of ions or atoms in a single the basis:
- The Sodium chloride structures Na and Cl ions are placed alternately in simple cubic bravias lattice structures. Each ion has six neighbour of other kind
- The Cesmium chloride structures Two BCC lattice intercaleted into each other Each ion has eight neighbour of other kind
- The Zincblende structures Zinc and sulfur atoms in a diamond lattice Each ion has four neighbour of other kind
5. Resources
- Crystal structure of Diamond lattice https://www.iue.tuwien.ac.at/phd/ungersboeck/node27.html